What Is BIOS In Computer And How Does It Work – Older desktop and laptop computers have a hidden software feature called BIOS. Making changes to the BIOS can improve how your computer works or prevent it from running properly.
What Is BIOS In Computer And How Does It Work 2024
But what is a BIOS? How do you access it, and what changes can you make while doing it? Here’s everything you need to know about your computer’s BIOS.
What is Bios?
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System is software that is stored on a small memory chip on the motherboard that can be replaced or upgraded. This chip is known as a Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS). Acts as an interface between the computer hardware and the operating system, allowing the software to control the hardware.
Read more:
- Best Ways to Fix Error 0x800F081F in Windows 10 PC
- 7 Ways To Fix Error Code 0xC0000225 In Windows 10 PC
- 8 Ways To Fix Error Code 0x8000FFFF in Windows 10 PC
- Difference Between APU CPU And GPU Complete Guide
This is low-level software that starts when you boot your computer. It performs a POST (power-on self-test), initializes your hardware, and passes control to the boot loader on the connected device. It then boots your operating system like Windows, Linux, or whatever you are using.
All of this is automatic, but the BIOS also has a settings screen, which you can access. Used to configure various low-level system settings, you can use it to manage things like:
- Boot orders
- Video memory
- Overclocking
- Virtualization
- power management
- Wake-on-LAN
- Fan management
- And much more…
Note that you shouldn’t change any settings in the BIOS unless you know what you’re doing. When you make a mistake while configuring it you can change the low-level CPU and memory which can make your computer unstable.
So, make sure you are familiar with your computer’s BIOS before saving any changes. Keep reading for tips for changing some of the most frequently used settings.
BIOS Functions
The BIOS has 4 main functions, namely:
- POST – Used to test the computer hardware and ensure that there are no errors before loading the operating system.
- Bootstrap Loader – Finds the operating system. If a capable operating system is found, the BIOS will give control to it.
- BIOS Drivers – Low-level drivers are systems that give your computer basic operational control over your computer hardware.
- BIOS setup or CMOS setup – A configuration program that allows you to configure hardware settings including system settings, such as computer passwords, time, and date.
How BIOS Works
When the computer boots, the CPU activates the BIOS ROM chip. The ROM BIOS then initiates a series of system checks, called the power-on self-test (POST). POST tells the CPU to check the bus (a series of connections that connect all PC components), memory (RAM), peripherals (keyboard, mouse, etc.), and disk drives.
This system check is quick and not very thorough. POST determines if everything is connected properly, but doesn’t check if everything is working perfectly. After the POST check is complete, the computer is ready to load the computer operating system.
At this point, users may notice that the light in drive A comes on again as the CPU checks to see if a bootable disk has been placed in the drive. Otherwise, find the operating system software there.
BIOS History
BIOS was invented in 1975 by a computer scientist named Gary Arlen Kildall. Before the BIOS came into existence, the operating system was the first software that was run when the computer was turned on. That means the computer can only run the default operating system.
In addition, the failure of the operating system makes the computer it is running on not work, because there is no other software that can fix it. After all, it cannot run before the operating system.
Kildall coined the term “BIOS” to describe the part of the machine that loads at boot and communicates with other hardware on the machine. BIOS provides added value flexibility, allowing users to install the operating system they want or to repair the current operating system if something goes wrong.
Popular BIOS Manufacturers
The following are some of the most popular BIOS vendors:
How to Access BIOS
To access the BIOS, restart your computer first. Press the appropriate key at the start of the boot-up process to access the BIOS setup screen. The key you need to press will appear on the screen at the start of the boot process. Note that if there is no keyboard attached to your PC, you cannot access the BIOS.
Usually, this is the Delete key, although some computers may use other keys such as F2, Esc(ape), F1, or F10. If you don’t know which key you need to press and it doesn’t appear on the screen, consult your computer manual. Alternatively, do a Google search for your computer model name and “BIOS key”.
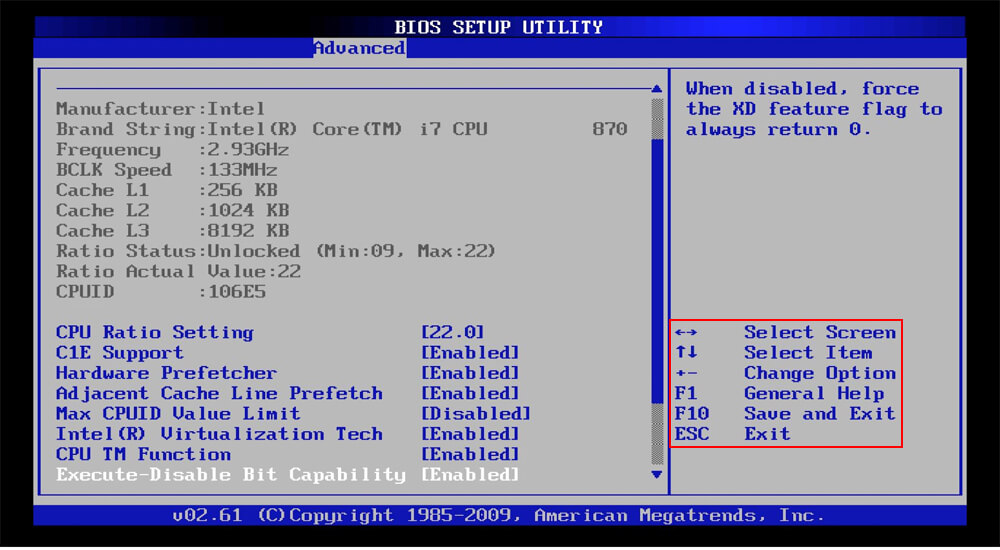
Note that each computer’s BIOS is different. Your computer’s BIOS may look very different from the screenshots here, or it may look similar but have different options.
To navigate the BIOS, use the arrow keys on your keyboard. A list of other keys that you need to use usually appears on the screen. Usually, you will use:
- Left and right arrow keys to switch between setting screens
- Up and down arrow keys to select an option on the current screen
- Enter to select an option or enter a sub-menu
- + and — keys to move items up and down in the list
If this sounds a bit complicated, it isn’t, you’ll mostly be using the arrow keys and Enter.
3 Most Common Settings Changed in BIOS
With access to the BIOS, you will find settings that you should ignore as well as some that may need to be changed. The most common BIOS settings for modification are:
- Changing the boot order
- Adjusting the available video memory
- Setting BIOS password
Here’s how to do each of these.
1. Boot Order
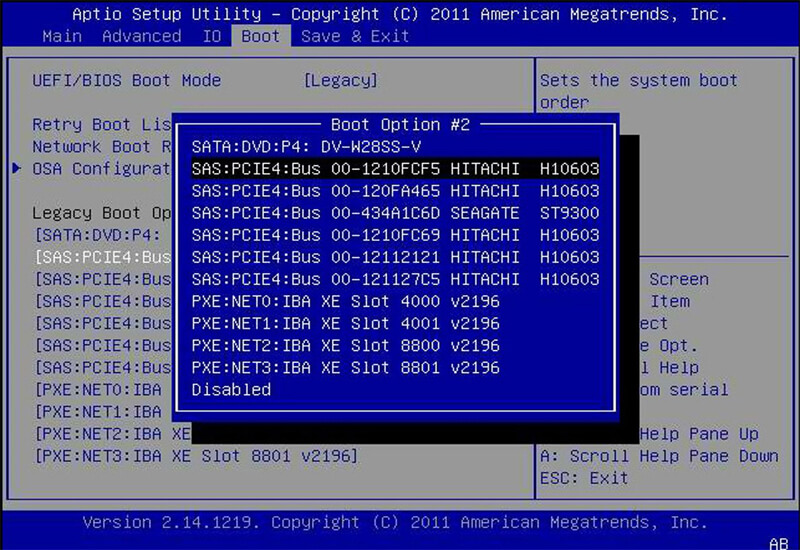
One of the most changed options in a computer’s BIOS is the boot order. After the BIOS starts and initializes your hardware, it passes control over to the boot loader that boots your operating system. The boot order determines which devices are controlled by the BIOS.
For example, you install Windows on your computer and a Linux live CD on your disk drive. (Or, a USB drive is plugged into your computer.) When you boot your computer, which operating system starts? The answer is determined by your boot order.
It is so-called because it controls the order in which the boot device checks for the OS. For example, a typical computer might have a DVD drive higher in the boot order list than an HDD. This means the computer will try to boot the operating system installation disc or live CD that was inserted first.
If there is no bootable disc in the DVD drive, the computer will try the next option on the list. This will most likely be the hard drive. You can boot your PC from:
- Optical drives (CD, DVD, Blu-ray, etc)
- USB drive (hard disk, thumb drive, or even USB optical drive)
- Network drives
If you want to boot another boot device, simply move it up in the boot order list. Usually, you’ll find a boot order on the screen called Boot or something similar. Use the + and — keys to reset the device in the boot order list.
Note: on some computers, USB drives may not appear in the list unless they are connected when you enter BIOS.
2. Video Memory
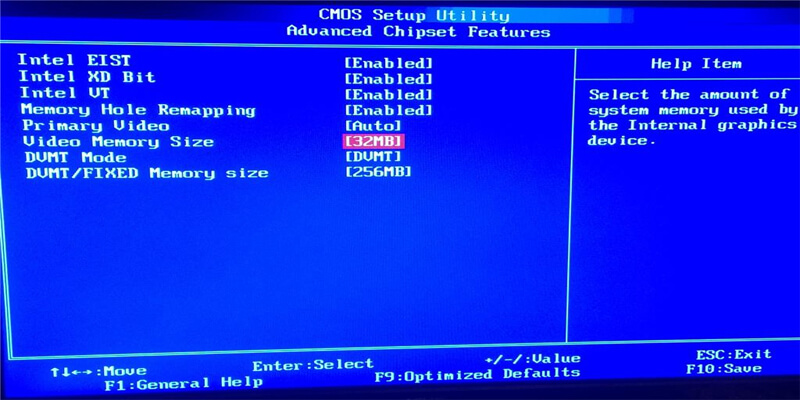
Computers with onboard graphics hardware, such as Intel integrated graphics, may have a Video Memory setting. The onboard graphics hardware does not have its own memory the way a dedicated graphics card does. Instead, it takes over a portion of the computer’s RAM and uses it as its video memory.
On some computers, the Video Memory option allows you to control how this memory is allocated. You can use this to allocate additional video memory or reduce it, reclaiming some of it for system tasks.
3. BIOS Password
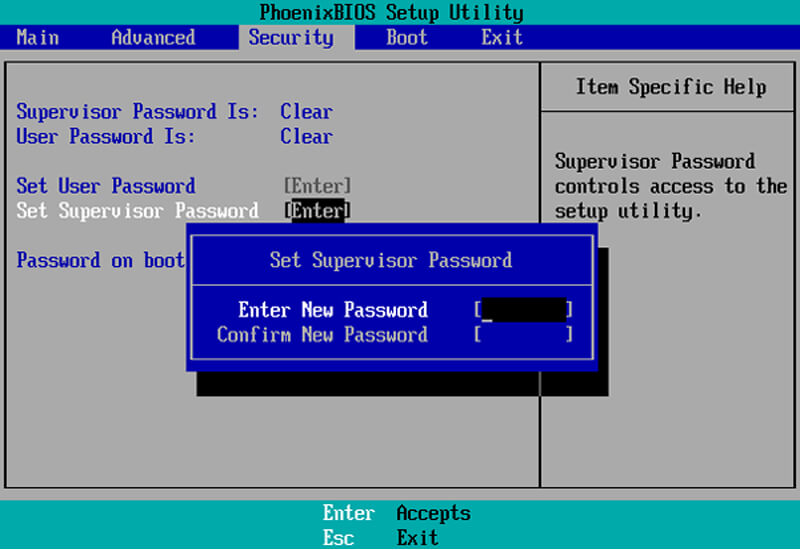
Although your operating system must have a login password, you can further secure your computer with a BIOS password. This can be set to control access to the BIOS, but you can also set a boot password.
With this enabled, no one can access the operating system or attached media. Be aware that this is not a perfect security feature. Anyone with physical access to your computer can reset the CMOS to clear this password.
What Do Save Changes And Reset In BIOS Do?
The changes you make to the BIOS settings do not take effect immediately. To save changes, look for the Save Changes and Reset option on the Save & Exit screen. This option saves your changes and then resets your computer.
There is also a Discard Changes and Exit option. This is selected if you make a mistake or decide you don’t want to change your BIOS settings at all. Just use this option to exit the BIOS setup screen without saving your changes. This option may have a slightly different name, but it is available in all BIOSes.
You can also use the appropriate keyboard shortcuts to save and exit quickly. Usually, this is F10 but again, it may be different in your BIOS.
What Happens When Selecting the Default Load Setup?
Your BIOS also contains the option Load Setup Defaults or Load Optimized Defaults. This option resets your BIOS to factory default settings, loading the default settings optimized for your hardware.
This performs a complete BIOS reset, removing any BIOS passwords apart from resetting your hardware settings and boot order. You probably won’t be using this, but it can be useful for quickly changing configurations after adding new hardware.
Other Less Common Settings Changed In BIOS
The BIOS contains several other settings and options. For example, there is a System Information screen that displays information about the hardware on your computer.
Overclockers may be able to use the CPU settings screen to change their CPU voltage and multiplier. This increases CPU performance but it can create additional heat, power usage, and possible instability. (However, some BIOSes lock this setting.)
Meanwhile, if your PC has support for virtualization, you can enable Hyper-V or Intel Virtualization Technology (or however it’s labeled) in the BIOS. For a full selection of settings that you can modify in the BIOS, check your computer or motherboard manual.
Read more:
- 8 Ways to Fix WHEA Uncorrectable Error Windows 10 PC
- What is the APU Accelerated Processing Unit? Complete Guide
- What is the difference between Unix and Linux
Conclusion:
So what is a BIOS? BIOS is low-level software, more precisely the first software that runs when you turn on the computer. The BIOS is a key component of any computer, and knowing how to use it can provide more flexibility and even performance benefits.
When configuring the BIOS, make sure you make your BIOS choices carefully. Because errors in BIOS settings can cause problems.
Don’t forget to bookmark and always visit every day Technowizah.com because you can find here the latest Tech Computer Android games How-to Guide Tips&Tricks Software Review etc, Which we update every day.


![6 Ways to Fix System Thread Exception Not Handled in Windows 10 [2024] 6 Ways to Fix System Thread Exception Not Handled in Windows 10](https://technowizah.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/6-Ways-to-Fix-System-Thread-Exception-Not-Handled-in-Windows-10-218x150.jpg)







![10+ Ways To Take Screenshot on Asus Laptop Windows 10 [2024] How To Take Screenshot on Laptop and PC Windows](https://technowizah.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/How-To-Take-Screenshot-on-Laptop-and-PC-Windows-100x70.jpg)
